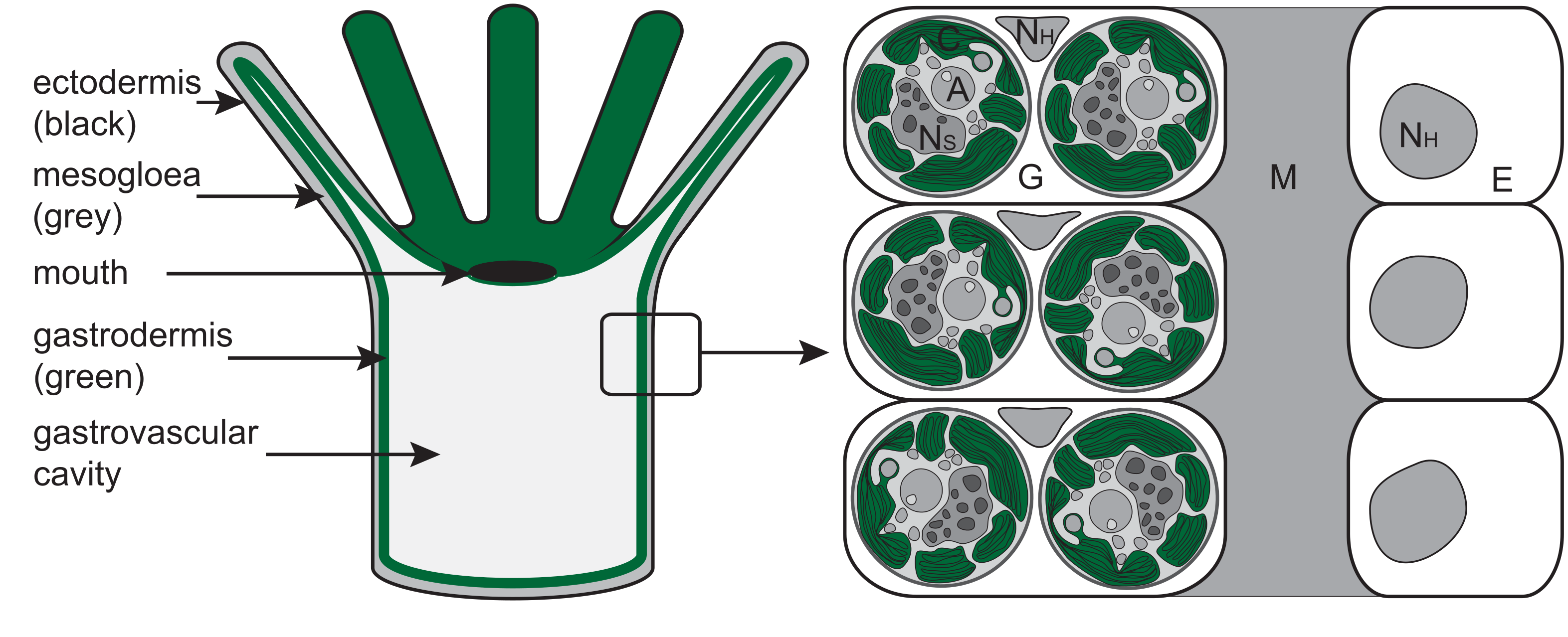
 Symbiotic zooxanthellae in the coral polyp gastroderm
Symbiotic zooxanthellae in the coral polyp gastroderm
 Symbiotic zooxanthellae in the coral polyp gastroderm
Symbiotic zooxanthellae in the coral polyp gastroderm
The symbiosis between corals and the dinoflagellate alga Symbiodinium is essential for the development and survival of coral reefs. Yet this fragile association is highly vulnerable to environmental disturbance. A coral's ability to tolerate temperature stress depends on the fitness of its resident symbionts, whose thermal optima vary extensively between lineages. However, the in hospite population genetic structure of Symbiodinium is poorly understood and mostly based on analysis of bulk DNA extracted from thousands to millions of cells. Using quantitative single-cell PCR, we enumerated DNA polymorphisms in the symbionts of the reef-building coral Pocillopora damicornis, and applied a model selection approach to explore the potential for recombination between coexisting Symbiodinium populations. RESULTS: Two distinct Symbiodinium ITS2 sequences (denoted C100 and C109) were retrieved from all P. damicornis colonies analysed. However, the symbiont assemblage consisted of three distinct Symbiodinium populations: cells featuring pure arrays of ITS2 type C109, near-homogeneous cells of type C100 (with trace ITS2 copies of type C109), and those with co-dominant C100 and C109 ITS2 repeats. The symbiont consortia of some colonies consisted almost entirely of these putative C100 × C109 recombinants. CONCLUSIONS: Our results are consistent with the occurrence of sexual recombination between Symbiodinium types C100 and C109. While the multiple-copy nature of the ITS2 dictates that the observed pattern of intra-genomic co-dominance may be a result of incomplete concerted evolution of intra-genomic polymorphisms, this is a less likely explanation given the occurrence of homogeneous cells of the C109 type. Conclusive evidence for inter-lineage recombination and introgression in this genus will require either direct observational evidence or a single-cell genotyping approach targeting multiple, single-copy loci.